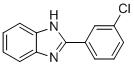
G 573
CAS No. 22868-35-5
G 573( G573 )
Catalog No. M13632 CAS No. 22868-35-5
G 573 is a potent and selective, allosteric inhibitor of MEK with Ki of 0.3 nM; blocks MEK phosphorylation by BRAF(V600E).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 873 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 1782 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 2250 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameG 573
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionG 573 is a potent and selective, allosteric inhibitor of MEK with Ki of 0.3 nM; blocks MEK phosphorylation by BRAF(V600E).
-
DescriptionG 573 is a potent and selective, allosteric inhibitor of MEK with Ki of 0.3 nM; blocks MEK phosphorylation by BRAF(V600E), and stabilizes the RAF-MEK complex; inhibits the proliferation of A375 (BRAF V600E) with IC50 of 11 nM, 15-fold less potent for HCT116 (KRAS G13D).
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsG573
-
PathwayMAPK/ERK Signaling
-
TargetMEK
-
RecptorMEK
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number22868-35-5
-
Formula Weight228.68
-
Molecular FormulaC13H9ClN2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESClC1=CC(C2=NC3=CC=CC=C3N2)=CC=C1
-
Chemical Name2-(3-Chlorophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Hatzivassiliou G, et al. Nature. 2013 Sep 12;501(7466):232-6.
molnova catalog



related products
-
BIX02189
BIX02189 is a potent, selective inhibitor of MEK5 catalytic activity with IC50 of 1.5 nM, also inhibits ERK5 catalytic activity (IC50=59 nM).
-
PD184161
PD184161 is a novel, orally-active MEK inhibitor.
-
Hederacolchiside A1
Hederacolchiside A1 shows anti-leishmanial activity it exhibits a strong antiproliferative activity on all stages of development of the parasite by altering membrane integrity and potential.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


